adapt.instance_based.KLIEP
- class adapt.instance_based.KLIEP(estimator=None, Xt=None, kernel='rbf', sigmas=None, max_centers=100, cv=5, algo='FW', lr=[0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0], tol=1e-06, max_iter=2000, copy=True, verbose=1, random_state=None, **params)[source]
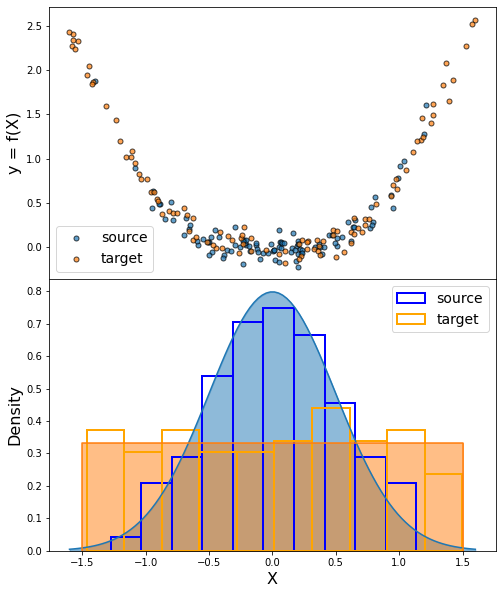
KLIEP: Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure
KLIEP is an instance-based method for domain adaptation.
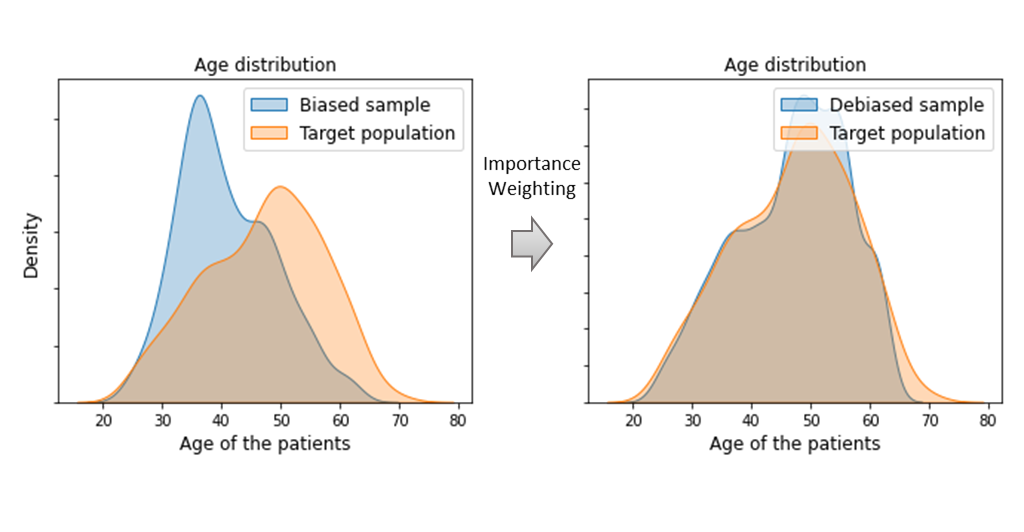
The purpose of the algorithm is to correct the difference between input distributions of source and target domains. This is done by finding a source instances reweighting which minimizes the Kullback-Leibler divergence between source and target distributions.
The source instance weights are given by the following formula:
\[w(x) = \sum_{x_i \in X_T} \alpha_i K(x, x_i)\]Where:
\(x, x_i\) are input instances.
\(X_T\) is the target input data.
\(\alpha_i\) are the basis functions coefficients.
\(K(x, x_i) = \text{exp}(-\gamma ||x - x_i||^2)\) for instance if
kernel="rbf".
KLIEP algorithm consists in finding the optimal \(\alpha_i\) according to the following optimization problem:
\[\max_{\alpha_i } \sum_{x_j \in X_T} \log( \sum_{x_i \in X_T} \alpha_i K(x_j, x_i))\]Subject to:
\[\sum_{x_j \in X_S} \sum_{x_i \in X_T} \alpha_i K(x_j, x_i)) = n_S\]Where:
\(X_S\) is the source input data of size \(n_S\).
The above OP is solved through gradient ascent algorithm.
Furthemore a LCV procedure can be added to select the appropriate parameters of the kernel function \(K\) (typically, the paramter \(\gamma\) of the Gaussian kernel). The parameter is then selected using cross-validation on the \(J\) score defined as follows: \(J = \frac{1}{|\mathcal{X}|} \sum_{x \in \mathcal{X}} \text{log}(w(x))\)
Finally, an estimator is fitted using the reweighted labeled source instances.
KLIEP method has been originally introduced for unsupervised DA but it could be widen to supervised by simply adding labeled target data to the training set.
- Parameters
- estimatorsklearn estimator or tensorflow Model (default=None)
Estimator used to learn the task. If estimator is
None, aLinearRegressioninstance is used as estimator.- Xtnumpy array (default=None)
Target input data.
- kernelstr (default=”rbf”)
Kernel metric. Possible values: [‘additive_chi2’, ‘chi2’, ‘linear’, ‘poly’, ‘polynomial’, ‘rbf’, ‘laplacian’, ‘sigmoid’, ‘cosine’]
- sigmasfloat or list of float (default=None)
Deprecated, please use the
gammaparameter instead. (See below).- cvint (default=5)
Cross-validation split parameter. Used only if sigmas has more than one value.
- max_centersint (default=100)
Maximal number of target instances use to compute kernels.
- algostr (default=”FW”)
Optimization algorithm. Possible values: [‘original’, ‘PG’, ‘FW’]
‘original’ follows the algorithm of [1]. Useful to reproduce the paper’s experiences.
‘PG’ is a improved version of ‘original’. A convex projection into the constraints set is used.
‘FW’ [2] uses the Frank-Wolfe algorithm to solve the above OP.
In general, ‘FW’ is more efficient than ‘original’ or ‘PG’. In some cases, ‘PG’ converges faster than ‘FW’ with a good choice of learning rate.
- lrfloat or list of float (default=np.logspace(-3,1,5))
Learning rate of the gradient ascent. Used only if algo different to ‘FW’
- tolfloat (default=1e-6)
Optimization threshold.
- max_iterint (default=2000)
Maximal iteration of the optimization algorithm.
- copyboolean (default=True)
Whether to make a copy of
estimatoror not.- verboseint (default=1)
Verbosity level.
- random_stateint (default=None)
Seed of random generator.
- paramskey, value arguments
Arguments given at the different level of the adapt object. It can be, for instance, compile or fit parameters of the estimator or kernel parameters etc… Accepted parameters can be found by calling the method
_get_legal_params(params).
- Yields
- gammafloat or list of float
Kernel parameter
gamma.For kernel = chi2:
k(x, y) = exp(-gamma Sum [(x - y)^2 / (x + y)])
For kernel = poly or polynomial:
K(X, Y) = (gamma <X, Y> + coef0)^degree
For kernel = rbf:
K(x, y) = exp(-gamma ||x-y||^2)
For kernel = laplacian:
K(x, y) = exp(-gamma ||x-y||_1)
For kernel = sigmoid:
K(X, Y) = tanh(gamma <X, Y> + coef0)
If a list is given, the LCV process is performed to select the best parameter
gamma.- coef0floaf or list of float
Kernel parameter
coef0. Used for ploynomial and sigmoid kernels. Seegammaparameter above for the kernel formulas. If a list is given, the LCV process is performed to select the best parametercoef0.- degreeint or list of int
Degree parameter for the polynomial kernel. (see formula in the
gammaparameter description). If a list is given, the LCV process is performed to select the best parameterdegree.
See also
References
- 1
[1] M. Sugiyama, S. Nakajima, H. Kashima, P. von Bünau and M. Kawanabe. “Direct importance estimation with model selection and its application to covariateshift adaptation”. In NIPS 2007
- 2
[2] J. Wen, R. Greiner and D. Schuurmans. “Correcting Covariate Shift with the Frank-Wolfe Algorithm”. In IJCAI 2015
Examples
>>> from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier >>> from adapt.utils import make_classification_da >>> from adapt.instance_based import KLIEP >>> Xs, ys, Xt, yt = make_classification_da() >>> model = KLIEP(RidgeClassifier(), Xt=Xt, kernel="rbf", gamma=[0.1, 1.], random_state=0) >>> model.fit(Xs, ys) Fit weights... Cross Validation process... Parameter {'gamma': 0.1} -- J-score = 0.013 (0.003) Parameter {'gamma': 1.0} -- J-score = 0.120 (0.026) Fit Estimator... >>> model.score(Xt, yt) 0.85
- Attributes
- weights_numpy array
Training instance weights.
- best_params_float
Best kernel params combination deduced from the LCV procedure.
- alphas_numpy array
Basis functions coefficients.
- centers_numpy array
Center points for kernels.
- j_scores_dict
dict of J scores with the kernel params combination as keys and the J scores as values.
- estimator_object
Fitted estimator.
Methods
__init__([estimator, Xt, kernel, sigmas, ...])fit(X, y[, Xt, yt, domains])Fit Adapt Model.
fit_estimator(X, y[, sample_weight, ...])Fit estimator on X, y.
fit_weights(Xs, Xt, **kwargs)Fit importance weighting.
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
predict(X[, domain])Return estimator predictions after adaptation.
predict_estimator(X, **predict_params)Return estimator predictions for X.
predict_weights([X])Return fitted source weights
score(X, y[, sample_weight, domain])Return the estimator score.
set_fit_request(*[, domains])Request metadata passed to the
fitmethod.set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
set_predict_request(*[, domain])Request metadata passed to the
predictmethod.set_score_request(*[, domain, sample_weight])Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.unsupervised_score(Xs, Xt)Return unsupervised score.
- __init__(estimator=None, Xt=None, kernel='rbf', sigmas=None, max_centers=100, cv=5, algo='FW', lr=[0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0], tol=1e-06, max_iter=2000, copy=True, verbose=1, random_state=None, **params)[source]
- fit(X, y, Xt=None, yt=None, domains=None, **fit_params)[source]
Fit Adapt Model.
For feature-based models, the transformation of the input features
XsandXtis first fitted. In a second stage, theestimator_is fitted on the transformed features.For instance-based models, source importance weights are first learned based on
Xs, ysandXt. In a second stage, theestimator_is fitted onXs, yswith the learned importance weights.- Parameters
- Xnumpy array
Source input data.
- ynumpy array
Source output data.
- Xtarray (default=None)
Target input data. If None, the Xt argument given in init is used.
- ytarray (default=None)
Target input data. Only needed for supervised and semi-supervised Adapt model. If None, the yt argument given in init is used.
- domainsarray (default=None)
Vector giving the domain for each source data. Can be used for multisource purpose.
- fit_paramskey, value arguments
Arguments given to the fit method of the estimator.
- Returns
- selfreturns an instance of self
- fit_estimator(X, y, sample_weight=None, random_state=None, warm_start=True, **fit_params)[source]
Fit estimator on X, y.
- Parameters
- Xarray
Input data.
- yarray
Output data.
- sample_weightarray
Importance weighting.
- random_stateint (default=None)
Seed of the random generator
- warm_startbool (default=True)
If True, continue to fit
estimator_, else, a new estimator is fitted based on a copy ofestimator. (Be sure to setcopy=Trueto usewarm_start=False)- fit_paramskey, value arguments
Arguments given to the fit method of the estimator and to the compile method for tensorflow estimator.
- Returns
- estimator_fitted estimator
- fit_weights(Xs, Xt, **kwargs)[source]
Fit importance weighting.
- Parameters
- Xsarray
Input source data.
- Xtarray
Input target data.
- kwargskey, value argument
Not used, present here for adapt consistency.
- Returns
- weights_sample weights
- get_metadata_routing()[source]
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
Not used, here for scikit-learn compatibility.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X, domain=None, **predict_params)[source]
Return estimator predictions after adaptation.
For feature-based method (object which implements a
transformmethod), the input featureXare first transformed. Then thepredictmethod of the fitted estimatorestimator_is applied on the transformedX.- Parameters
- Xarray
input data
- domainstr (default=None)
For antisymetric feature-based method, different transformation of the input X are applied for different domains. The domain should then be specified between “src” and “tgt”. If
Nonethe default transformation is the target one.
- Returns
- y_predarray
prediction of the Adapt Model.
- predict_estimator(X, **predict_params)[source]
Return estimator predictions for X.
- Parameters
- Xarray
input data
- Returns
- y_predarray
prediction of estimator.
- predict_weights(X=None)[source]
Return fitted source weights
If
None, the fitted source weights are returned. Else, sample weights are computing using the fittedalphas_and the chosencenters_.- Parameters
- Xarray (default=None)
Input data.
- Returns
- weights_sample weights
- score(X, y, sample_weight=None, domain=None)[source]
Return the estimator score.
If the object has a
transformmethod, the estimator is applied on the transformed features X. For antisymetric transformation, a parameter domain can be set to specified between source and target transformation.Call score on sklearn estimator and evaluate on tensorflow Model.
- Parameters
- Xarray
input data
- yarray
output data
- sample_weightarray (default=None)
Sample weights
- domainstr (default=None)
This parameter specifies for antisymetric feature-based method which transformation will be applied between “source” and “target”. If
Nonethe transformation by default is the target one.
- Returns
- scorefloat
estimator score.
- set_fit_request(*, domains: Union[bool, None, str] = '$UNCHANGED$') adapt.instance_based._kliep.KLIEP[source]
Request metadata passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config()). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters
- domainsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
domainsparameter infit.
- Returns
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_params(**params)[source]
Set the parameters of this estimator.
- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_predict_request(*, domain: Union[bool, None, str] = '$UNCHANGED$') adapt.instance_based._kliep.KLIEP[source]
Request metadata passed to the
predictmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config()). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed topredictif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it topredict.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters
- domainstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
domainparameter inpredict.
- Returns
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_score_request(*, domain: Union[bool, None, str] = '$UNCHANGED$', sample_weight: Union[bool, None, str] = '$UNCHANGED$') adapt.instance_based._kliep.KLIEP[source]
Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config()). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toscoreif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toscore.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters
- domainstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
domainparameter inscore.- sample_weightstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
sample_weightparameter inscore.
- Returns
- selfobject
The updated object.